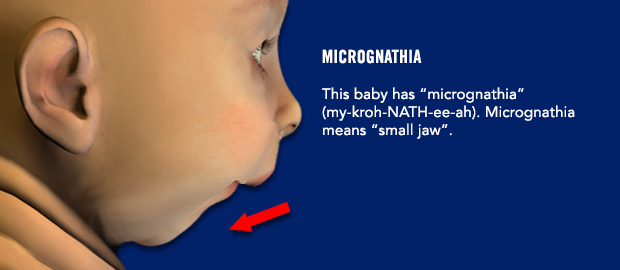
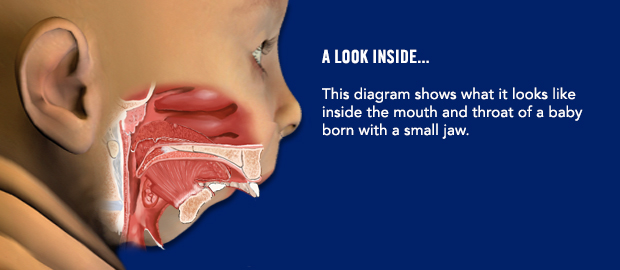
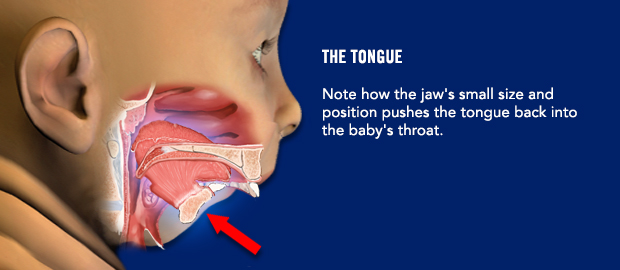
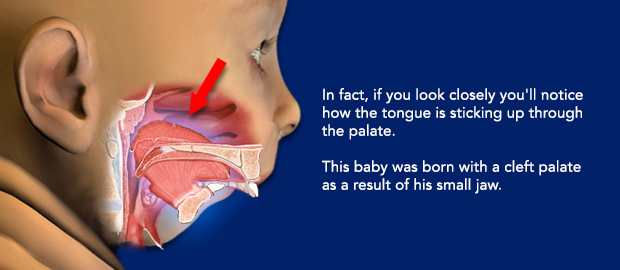
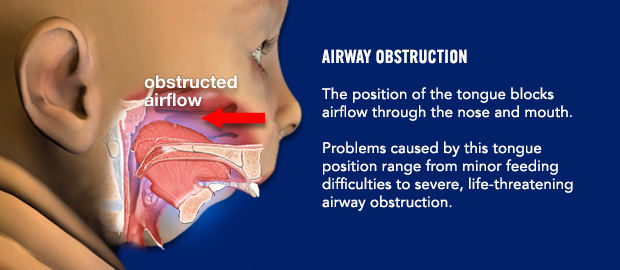
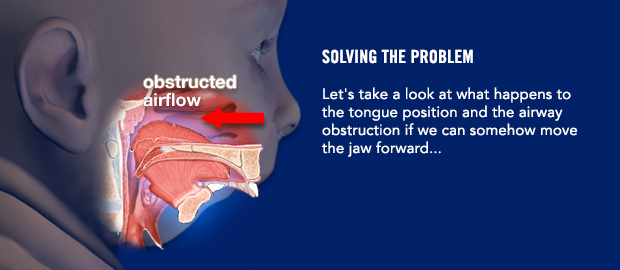
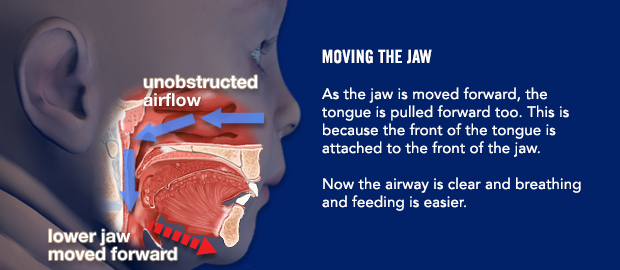
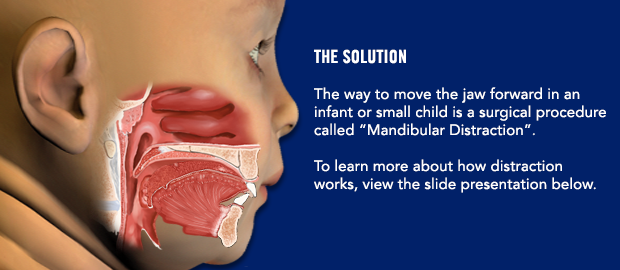
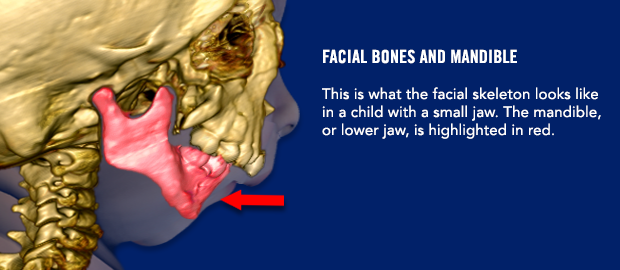
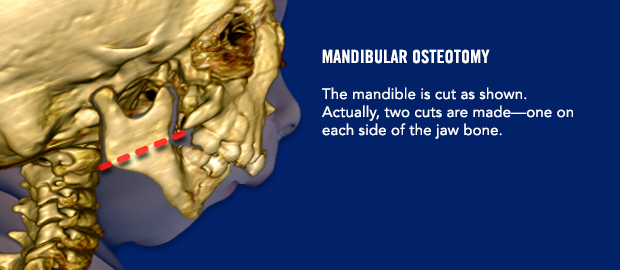
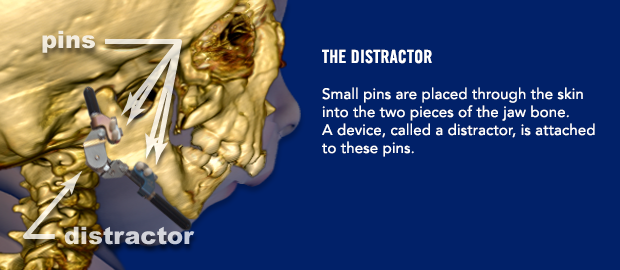
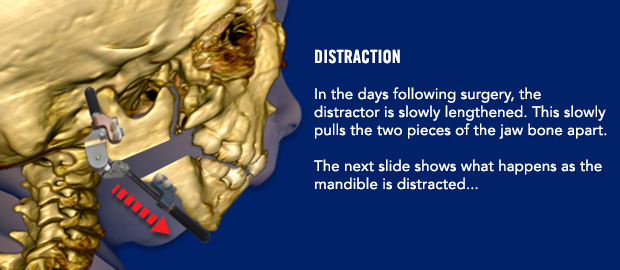
Are there any instructions I need to follow before surgery?
Most children who undergo mandibular distraction are still in the hospital when the procedure is performed. If your child is at home before having surgery your child must have a physical examination by his or her pediatrician or family doctor within 7 days before surgery to make sure he or she is in good health. The doctor you see needs to complete the History and Physical form provided by our office. You must bring the completed form with you the day of surgery.
For your child’s safety, it is very important that he or she have an empty stomach when anesthesia is given. Please follow our preoperative Eating and Drinking Guidelines. If you do not follow these guidelines, your child’s surgery will be cancelled.
What can I expect after surgery?
The procedure usually takes between 2 and 4 hours. Your child will be taken to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) following surgery. It is common for your child to remain on a ventilator after surgery. The amount of time your child will need to stay on the ventilator depends on how much trouble your child had breathing before surgery. But don’t worry…your child will soon breathe without the ventilator.
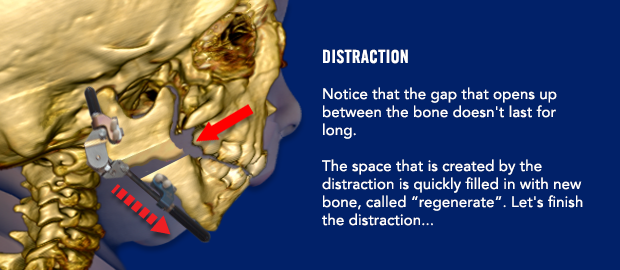
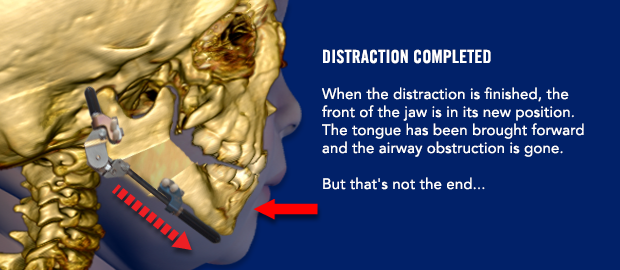
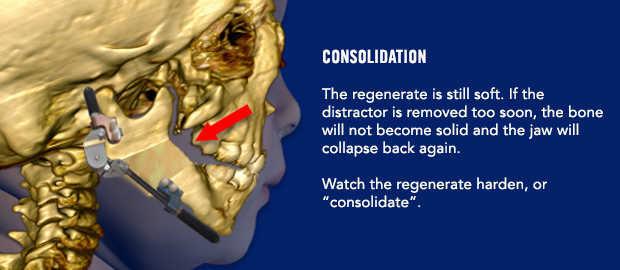
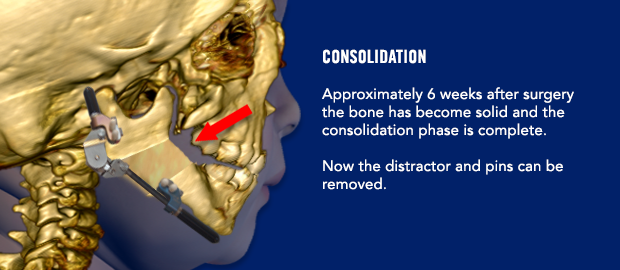
The distraction process will begin 3 days after surgery. It important to wait a few days before starting the distraction process. On post-operative day 3, your surgeon will begin moving the jaw forward by turning a screw on the front of each distractor. The nurses will learn how to continue the distraction process. You may also learn how to perform the distractions yourself if your child will be discharged from the hospital before the distraction is complete. Yes, some children don’t need to stay in the hospital during the distraction process! Don’t worry…it is not difficult to learn how to distract your child’s jaw.
Does it hurt?
Your child will certainly have pain and discomfort for a few days after surgery. This will be controlled with pain medication. After just a few days, the pain will subside and only mild pain medication like Tylenol® may be required from time to time.
Many parents and nurses are concerned that the process of distracting the jaw is painful; however, this is not the case. The jaw bones are separated less than 1 mm each time the screws are turned. This is less than the thickness of a United States quarter! We know that distraction is not painful—many older children have had this procedure done and report no significant pain during the daily distractions.
Answers to other frequently asked questions…
Mandibular distraction is a very specialized surgical treatment for infants and children with special problems. It is not a routine part of most surgeons’ practice. The doctors at Children’s ENT and Facial Plastic Surgery have specialized knowledge and experience caring for children in need of mandibular distraction. We have performed more of these procedures than any other surgeons in the region, and possibly the country. But more importantly, we know when and when not to recommend this procedure.
Every child is unique and mandibular distraction is a major surgical procedure with potential risks. Your doctor will spend as much time as necessary to discuss your child’s particular problems and why distraction may or may not be an option worth consideration.