Vulvovaginitis
What is Vulvovaginitis?
Vulvovaginitis is irritation that affects the vagina or the outer genital area (the vulva). A young personwith vulvovaginitis may experience redness, soreness, burning, itching, discomfort, or vaginal discharge. While it may be upsetting, the condition is not serious and will not affect future reproduction.
What causes Vulvovaginitis?
Before puberty there is no pubic hair or prominent, adult-type labia. The vulva does not have protection against outside irritants. . Also, before puberty, your child lacks a hormone called estrogen to defend their reproductive tract so the pH of the vagina is high, which can allow overgrowth of bacteria. There are many possible causes of vulvovaginitis. The most common are:
- Irritation of the genital area, due to soaps, detergents, chemicals (chlorine, bubble bath, bath bombs), poor hygiene practices (pee, poop), and tight clothing
- Infections, for example with bacteria from the mouth, nose, or from the anus
- Skin conditions, such as eczema
- Foreign bodies (objects, like toilet paper) stuck in the vagina
See a health care clinician who can find out the cause of the problem.
Prevention and treatment
- Teach good hygiene
-
Wash hands before and after using the bathroom.
-
Avoid constipation. If your child is not having a soft, daily bowel movement they may have constipation and require treatment. Discuss this with your doctor.
- Wipe from front to back after peeing or pooping.
- Pee with knees spread apart while leaning forward and stay seated on the toilet until finished urinating to allow all the pee to come out. For smaller children, it also might be helpful for them to sit backwards on the toilet (facing the tank) so they feel more supported.
- Take a plain water bath (not a shower) every day. Soak in a frog-leg position in a tub of plain, warm (not hot) water for 10 minutes daily.
- Avoid irritation
- Wear cotton underwear during the day and avoid wearing underwear at night.
- Avoid harsh laundry detergents and make sure underwear is rinsed thoroughly. Avoid fabric softeners and dryer sheets.
- Do not use bubble bath or add anything else to bath water unless prescribed by your doctor.
- Avoid using soap in the sensitive vulvar area; this area can be cleansed with a soft cloth and water alone. Use a mild, hypoallergenic bar cleanser, such as unscented Dove® on the rest of the body. Avoid deodorant soaps.
- Make sure all cleansers are washed off after bathing, and do not allow cleansers or shampoo to float around in the bathtub. Your child should stand in the tub when using soaps instead of sitting in the soapy water.
- Avoid tight jeans or pants, and tights.
- Avoid sitting in a wet bathing suit after swimming – rinse chlorine off of the vulvar area after swimming and change as soon as possible into dry clothing.
- You can try applying a protective ointment, like petroleum jelly(Vaseline) or zinc oxide paste (Desitin), if recommended by your provider.
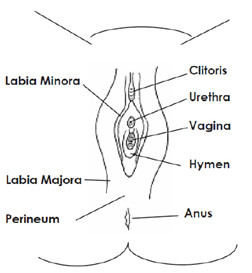
Genital area of a young patient
After treatment
- Go to the follow-up appointment, even if the symptoms are better. We want to be sure you are better.
- Continue baths and focus on appropriate vulvar care. Symptoms may reoccur until puberty unless hygiene recommendations are followed or if children are exposed to irritants again.
Call the office if your child has any of the following:
- Your child’s symptoms are not getting better.
- You notice vaginal bleeding.
- Your child has pain or burning when urinating, and is urinating more often.
- You have other concerns or questions.
- Symptoms return.
Specific treatments for your child’s condition (follow only if directed by your provider):
Topical creams/ointments:
____ Clindamycin cream/Metronidazole Gel
____ Steroid ointment
Antibacterial solution:
____ Add ¼ cup Hibiclens® liquid soap to bath water 1 to 2 times a week. Rinse off with fresh water.
____ Bleach bath recipe for skin conditions: Add ¼ cup concentrated household beach (~8% sodium hypochlorite) or ½ cup of common household bleach (~6% sodium hypochlorite) to a bathtub full of water. Soak the affected part of the skin for about 10 minutes. Limit diluted bleach baths to no more than twice a week. Do not submerge head and be very careful to avoid getting the diluted bleach into eyes. Rinse off with fresh water.
Questions?
This information is general and not specific to your child. If you have questions, please contact your health care professional.
Reviewed by GYN 7/2022
This page is not specific to your child, but provides general information on the topic above. If you have any questions, please call your clinic. For more reading material about this and other health topics, please call or visit Children's Minnesota Family Resource Center library, or visit www.childrensmn.org/educationmaterials.
© 2024 Children's Minnesota
