Appendicitis (Possible)
What is the appendix?
The appendix is a hollow tube-like structure connected to the large bowel. The appendix is about the size of a finger and in most cases is located in the right lower part of the abdomen (belly). There is no known benefit of an appendix even though everyone is born with one. Removal of the appendix does not cause a problem with how our bowel works.
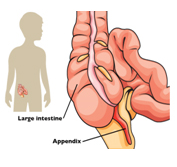
What is appendicitis?
The appendix can become large and swell when it is irritated or becomes infected. This happens when the appendix clogs with mucus, poop, or intestinal stones (fecalith). Germs from the bowel quickly grow in the appendix, enter the wall of the appendix, and cause the body to send pus cells (inflammation) to the appendix to stop infection. The appendix then becomes red, swollen, and begins to hurt more and more. Boys tend to develop appendicitis more than girls but it is not known why. There is no known way to prevent appendicitis but a fiber-rich diet may help prevent it. Appendicitis can develop at any age but often develops in children 10 years old and older.
What are the symptoms of appendicitis?
Every child is different, but in most cases, symptoms develop over 24 – 48 hours.
- Discomfort in the area of the belly button
- Loss of interest in eating or drinking
- Feeling sick to stomach
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Loss of interest in activity due to discomfort or pain
- Discomfort turning into pain in the lower right corner of the abdomen
- Dehydration (if vomiting or not drinking)
- Pain with movement and walking
How is appendicitis diagnosed?
There are many causes of stomach pain and appendicitis is sometimes hard to diagnose right away. To help find out what is causing the pain, your provider may:
- Ask about symptoms
- Perform a physical examination
- Collect blood to look for infection
- Use a painless test called ultrasound
- Sometimes, use a CT scan
If your provider is still unsure about the diagnosis, your child will stay at the hospital until it is clear what is causing the pain.
How is appendicitis treated?
Once appendicitis is diagnosed, three treatments will be provided through an intravenous (IV).
- Pain medicine
- If your child is dehydrated from fever and vomited, fluids will be provided
- Antibiotics
These three treatments will help the child feel better and best prepare the child for surgery to remove the appendix. Removing the appendix through an operation called appendectomy, will help make sure appendicitis doesn’t happen again.
Questions?
This is not specific to your child but provides general information. If you have questions, please call your clinic.
This page is not specific to your child, but provides general information on the topic above. If you have any questions, please call your clinic. For more reading material about this and other health topics, please call or visit Children's Minnesota Family Resource Center library, or visit www.childrensmn.org/educationmaterials.
© 2024 Children's Minnesota
