A to Z Symptom: Fainting
May also be called: Syncope; Swooning; Passing Out
More to Know
In most cases, fainting — or syncope (SIN-ko-pee) — is not a sign of a dangerous problem.
Causes
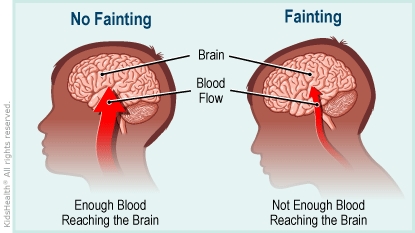
Fainting is a temporary loss of consciousness. It happens when not enough blood reaches the brain due to a fall in blood pressure.
Common causes include dehydration, a quick change in position, standing or sitting still for a long period, becoming overheated, hyperventilation (overbreathing), low blood sugar, anemia, sudden fear of something (for example, the sight of blood), and some heart problems.
Most cases have warning signs (such as a change in vision, dizziness, nausea, or stomach pain) that happen a few seconds before passing out.
Treatment
Fainting in children, especially teens, is common but shouldn't be ignored. Discuss it with your doctor, especially if it happens during exertion (exercising, running, etc.) or happens often.
Keep in Mind
When warning signs of fainting happen, quickly sitting down, dropping the head between the knees, or lying down on the floor may help avoid a loss of consciousness. Then, gradually get up after the dizzy feeling has passed.
All A to Z dictionary entries are regularly reviewed by KidsHealth medical experts.
Note: All information is for educational purposes only. For specific medical advice, diagnoses, and treatment, consult your doctor.
© 1995-2024 KidsHealth ® All rights reserved. Images provided by iStock, Getty Images, Corbis, Veer, Science Photo Library, Science Source Images, Shutterstock, and Clipart.com

