Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Article Translations: (Spanish)
What Is Eczema?
Eczema is a condition where the skin gets irritated, red, dry, bumpy, and itchy. There are several types of eczema, but the most common is atopic dermatitis. To many people, "eczema" and "atopic dermatitis" mean the same thing.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Eczema?
The signs of eczema (EK-zeh-ma):
- are mainly dry, itchy skin. Because it is so itchy, it is often called "the itch that rashes."
- include redness, scales, and bumps that can leak fluid and then crust over
- tend to come and go. When they get worse, it is called a flare-up.
- may be more noticeable at night
Symptoms can vary:
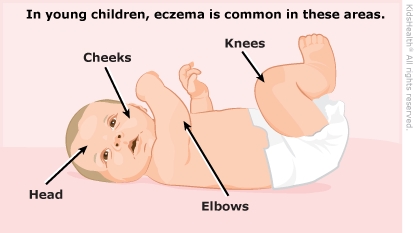
- Infants younger than 1 year old usually have the eczema rash on their cheeks, forehead, or scalp. It may spread to the knees, elbows, and trunk (but not usually the diaper area).
- Older kids and teens usually get the rash in the bends of the elbows, behind the knees, on the neck, or on the inner wrists and ankles. Their skin is often scalier and drier than when the eczema first began. It also can be thicker, darker, or scarred from all the scratching (called lichenification).
What Causes Eczema?
Doctors don't know exactly what causes eczema. It might be that there's a difference in the way a person's immune system reacts to things. Skin allergies may be involved in some forms of eczema.
Who Gets Eczema?
Many kids and teens with eczema have family members who have it. Experts think it passes from parents to kids through genes. Eczema is fairly common.
People with eczema also may have asthma and some types of allergies, such as hay fever. Eczema, asthma, and hay fever are known as "atopic" conditions. These affect people who are overly sensitive to allergens in the environment. For some, food allergies may bring these on or make them worse. For others, allergies to animal dander, dust, pollen or other things might be the triggers.
Eczema is not contagious.
How Is Eczema Diagnosed?
There is no specific test used to diagnose eczema. The doctor will look at the rash and ask about symptoms, the child's past health, and the family's health. If family members have any atopic conditions, that's an important clue.
The doctor will rule out other conditions that can cause skin inflammation, and might recommend that your child see a dermatologist or an allergist.
The doctor may ask you to ban some foods (such as eggs, milk, soy, or nuts) from your child's diet, switch detergents or soaps, or make other changes for a time to see if your child is reacting to something.
How Is Eczema Treated?
There is no cure for eczema. But treatments can help with symptoms. The doctor will recommend different treatments based on how severe the symptoms are, the child's age, and where the rash is. Some are "topical" and applied to the skin. Others are taken by mouth.
Topical moisturizers. Skin should be moisturized often (ideally, two or three times a day). The best time to apply moisturizer is after a bath or shower, with the skin patted dry gently. Ointments (such as petroleum jelly) and creams are best because they contain a lot of oil. Lotions have too much water to be helpful.
Topical corticosteroids, also called cortisone or steroid creams or ointments. These ease skin inflammation. (These aren't the same as steroids used by some athletes.) It's important not to use a topical steroid prescribed for someone else. These creams and ointments vary in strength, and using the wrong strength in sensitive areas can damage the skin, especially in infants.
Other topical anti-inflammatory medicines. These include medicines that change the way the skin's immune system reacts.
Medicine taken by mouth. These can include antihistamines (anti-allergy medicine) to help itchy kids sleep better at night, antibiotics if a rash gets infected by bacteria, and corticosteroid pills or other medicines that suppress the immune system.
Other types of treatment can include:
- phototherapy: treatment with ultraviolet light
- wet wraps: damp cloths placed on irritated areas of skin
- bleach baths: bathing in very diluted bleach solution
How Can Parents Help?
Help prevent or treat eczema by keeping your child's skin from getting dry or itchy and avoiding triggers that cause flare-ups. Try these suggestions:
- Kids should take short baths or showers in warm (not hot) water. Use mild unscented soaps or non-soap cleansers and pat the skin dry before putting on cream or ointment. Teens should use unscented makeup and oil-free facial moisturizers.
- Ask your doctor if it's OK to use oatmeal soaking products in the bath to help control itching.
- Kids should wear soft clothes that "breathe," such as those made from cotton. Wool or polyester may be too harsh or irritating.
- Keep your child's fingernails short to prevent skin damage from scratching. Try having your child wear comfortable, light gloves to bed if scratching at night is a problem.
- Kids should avoid becoming overheated, which can lead to flare-ups.
- Kids should drink plenty of water, which adds moisture to the skin.
- Get rid of known allergens in your household and help your child avoid others, like pollen, mold, and tobacco smoke.
- Stress can make eczema worse. Help your child find ways to deal with stress (like exercise, deep breathing, or talking to a counselor).
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Children and teens with eczema are prone to skin infections. Call your doctor right away if you notice any early signs of skin infection, such as
- fever
- redness and warmth on or around affected areas
- pus-filled bumps on or around affected areas
- areas on the skin that look like cold sores or fever blisters
Also call your doctor if you notice a sudden change or worsening of the eczema, or if it isn't responding to the doctor's recommendations.
What Else Should I Know?
For many kids, eczema begins to improve by the age of 5 or 6. Sometimes it goes away. In other kids, it may start again as they enter puberty. Some people still have eczema as adults, with areas of itching that look dry and scaly.
Note: All information is for educational purposes only. For specific medical advice, diagnoses, and treatment, consult your doctor.
© 1995-2024 KidsHealth ® All rights reserved. Images provided by iStock, Getty Images, Corbis, Veer, Science Photo Library, Science Source Images, Shutterstock, and Clipart.com

