Cushing Syndrome
Article Translations: (Spanish)
What Is Cushing Syndrome?
Cushing syndrome is a rare condition that happens when there's too much of the hormonecortisol in the body. It's also called hypercortisolism.
Most cases of Cushing syndrome happen in adults 25 to 40 years old, and it's more common in women than men.
What Is Cortisol?
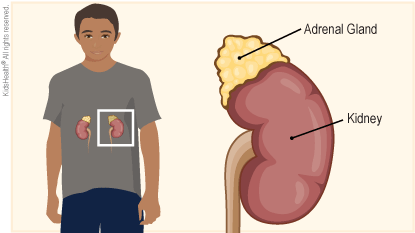
Cortisol (KOR-tih-sol) is a type of glucocorticoid (gloo-koh-KOR-tih-koyd) hormone made by the two adrenal glands . The adrenal glands are small organs that sit on top of the kidneys.
Cortisol made by the body:
- converts sugar, fat, and protein into energy
- stimulates glucose production
- regulates blood pressure
- helps prevent swelling and inflammation
- suppresses immune system responses
It's often called the "stress hormone" because cortisol gives our bodies the energy to fight stress, such as a fever, illness, injury, or a dangerous situation (the "fight-or-flight" response). It signals the body to speed up the metabolism of stored sugar, fat, and protein, turning these into energy.
Doctors use manmade cortisol, or hydrocortisone, to treat asthma, allergies, and inflammation.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Cushing Syndrome?
Symptoms of Cushing syndrome might take months to develop. They can include:
- a round face
- a fatty hump between the shoulders and neck
- weight gain
- growth problems
- red or purple stretch marks
- thin skin that bruises easily
- tiredness
- acne
- high blood pressure
- type 2 diabetes
- thicker, more noticeable facial hair in girls (hirsutism)
- bone problems
- muscle weakness
- behavior changes
What Causes Cushing Syndrome?
Cushing syndrome can happen if someone takes large amounts of corticosteroid drugs, such as prednisone. This is known as exogenous (ek-SAH-jeh-nis) Cushing syndrome.
Someone might take oral corticosteroids (pills taken by mouth) to:
- treat an inflammatory disease such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or asthma
- prevent the body from rejecting a transplanted organ
Less often, a corticosteroid applied to the skin (for instance, to treat eczema) or inhaled (to treat asthma) can lead to Cushing syndrome if used in very high doses.
Cushing syndrome also can happen if the body makes too much cortisol. This is known as endogenous (en-DAH-jeh-nis) Cushing syndrome.
In children, Cushing syndrome usually happens because of:
- a problem in the adrenal gland that makes it produce too much cortisol
- a problem in the pituitary gland
- an adrenal tumor (most of these are not cancerous)
How Is Cushing Syndrome Diagnosed?
A doctor may suspect Cushing syndrome if a person has the telltale signs, such as a rounded face, a pad of fatty tissue between the shoulders, thin skin with bruises and stretch marks, and poor growth.
In children, doctors might suspect Cushing syndrome when a child is gaining weight but not growing as expected.
The doctor will do a physical exam and ask if the child has been taking a corticosteroid medicine for a long time. In kids not taking a corticosteroid medicine, doctors might order tests. These can include:
- 24-hour urinary free-cortisol test: a urine test that collects urine (pee) for 24 hours to measure hormone levels
- a diurnal cortisol test: measuring cortisol in a blood or saliva (spit) sample
- a low-dose dexamethasone suppression test: doing a blood test to measure cortisol after the child takes a glucocorticoid
- a CRH stimulation test: doing repeated blood draws over several hours to measure cortisol levels after the child gets a shot of corticotropin-releasing hormone
How Is Cushing Syndrome Treated?
A pediatric endocrinologist will oversee the care of a child with Cushing syndrome. Depending on what's causing it, treatment for Cushing syndrome might involve:
- surgery to remove tumors or growths on the adrenal or pituitary glands
- radiation therapy to treat tumors or growths on the adrenal glands
- changing how much or how often a child takes a corticosteroid medicine
- taking drugs that block the production of hormones
What Else Should I Know?
Children with Cushing syndrome will have follow-up visits with their pediatric endocrinologist every 3–6 months. The doctor will check hormone levels, adjust medicines as needed, and see if symptoms have improved. To do this, the doctor might:
- order blood tests and urine tests
- see if the child is reaching the expected height and weight goals
Note: All information is for educational purposes only. For specific medical advice, diagnoses, and treatment, consult your doctor.
© 1995-2024 KidsHealth ® All rights reserved. Images provided by iStock, Getty Images, Corbis, Veer, Science Photo Library, Science Source Images, Shutterstock, and Clipart.com

