Choking (age 1 and older)
Article Translations: (Spanish) (Hmong) (Somali)
Translations available: Spanish
How can I prevent choking?
Choking can happen to anyone and often can be prevented. Many foods and foreign bodies have been the cause of choking in children and some adults. It often happens when people try to swallow large, poorly chewed pieces of food, such as meat. Ways to prevent choking include:
- Cut up food into small pieces.
- Chew food well.
- If something is hard to chew, remove it from your mouth. Do not swallow it.
- Do not allow children to run, play, laugh, or talk with food in their mouth.
- Do not put small objects in your mouth.
What are the signs of choking?
- person clutches his or her neck
- high-pitched noisy breathing
- cough is very quiet
- cannot talk or make sounds
- color changes from red to purple to blue
- cannot breathe
What should I do?
Ask, "Are you choking?"ÂÂ If person nods yes, say you're going to help. Follow these steps until the object comes out and the person can breathe, cough, or talk, or does not respond.
Abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver):
- Stand or kneel behind the person and put your arms under his or her arms.
- Put the thumb-side of your fist against the person's abdomen (belly) just above the belly button. Place your other hand over your fist.
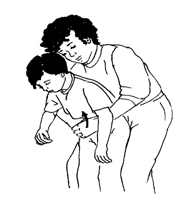
- Press into the abdomen with quick inward and upward thrusts.
If the person does not respond
- Yell, "Help - Call 911!"
- Do CPR, but each time you open the airway to give breaths, look for an object in the mouth. If you see something, remove it. If nothing is seen, do not put your fingers in the mouth.
- Continue CPR until the person responds, or trained help takes over.
Important
This information is a review of techniques taught in a class on managing choking. It is not complete in itself. You must practice these techniques on a manikin with an instructor. Do not practice techniques on a person.
Last Reviewed Respiratory 7/2015 ©Copyright
This page is not specific to your child, but provides general information on the topic above. If you have any questions, please call your clinic. For more reading material about this and other health topics, please call or visit Children's Minnesota Family Resource Center library, or visit www.childrensmn.org/educationmaterials.
© 2024 Children's Minnesota
